In a recent project, Farhad Hormozdiari and Eleazar Eskin contributed data analysis and interpretation to a project identifying new genes and genomic regions associated with metabolic function in mice. Our paper presents a comprehensive picture of the transcriptome of the mouse hypothalamus and its genetic variation and regulation. This project, which was published in eLife, was led by fellow UCLA researchers Yehudit Hasin-Brumshtein, Jake Lusis, and Desmond Smith.
Mice and humans share virtually the same set of genes; thus, mapping the mouse genome is an important step toward understanding genetic factors in common, complex human diseases such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. In metabolic tissues, the integration of genome-wide expression profiles with genetic and phenotypic variance can provide valuable insight into a disease’s underlying molecular mechanism. Measuring gene activity can reveal new molecules that clinical translation efforts may target to treat metabolic disorders.
Our project uses RNA-Seq to characterize transcriptome in 99 inbred strains of mice from the Hybrid Mouse Diversity Panel (HMDP), a reference resource population for cardiovascular and metabolic traits. Mice were fed a high, high sugar diet, and all strains were comprehensively genotyped and phenotyped for 150 metabolic traits. Our study examines tissues relevant to the hypothalmus, the brain region that controls metabolism and regulates body weight and appetite.
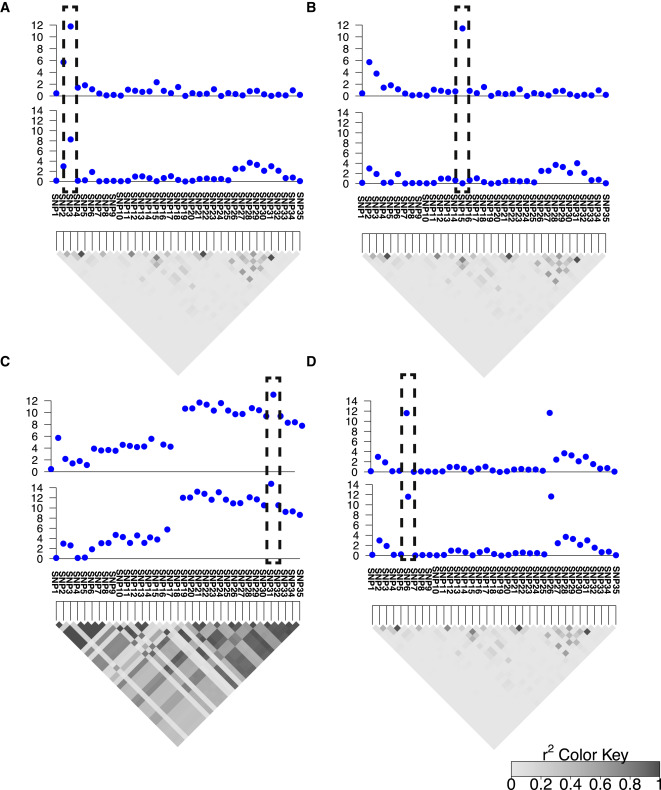
We sequenced 285 samples from all 99 strains of the HMDP. Using methods described in our paper, we identified thousands of new isoforms and >400 new genes. The HMDP allowed us to map Quantitative Trait Loci (eQTLs) with high resolution and power, identifying both local and trans acting variants—or, variants that affect a molecule from within and from outside, respectively.
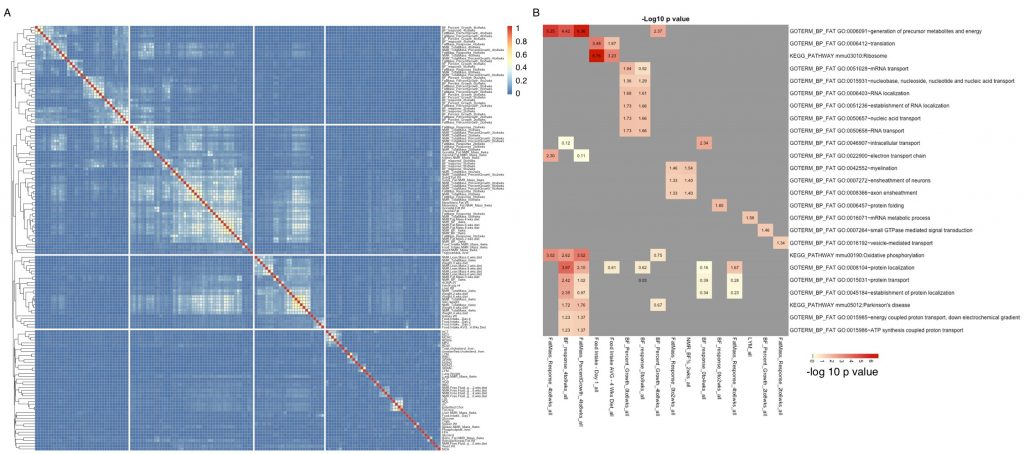
Groups of genes are associated with multiple related phenotypes in HMDP, although not necessarily enriched for GO ontology or specific pathways. For more information, see our paper.
We report numerous novel transcripts supported by proteomic analyses, as well as novel non-coding RNAs. High resolution genetic mapping of transcript levels in HMDP reveals both local and trans expression eQTLs, identifying two trans eQTL ’hotspots’ associated with expression of hundreds of genes. We also report thousands of alternative splicing events regulated by genetic variants. We further showed that the genes associated with trans eQTL hotspots correlate to physiological phenotypes, such as HDL and triglyceride levels. This discovery provides insight into the mechanism behind correlation of these genotypes with complex traits.
Our data capture the various non-neuronal cell types, such as microglia or astrocytes, which are often overlooked in the mostly neuron focused studies of the hypothalamus. These cells are important mediators of hypothalamic inflammation and other processes induced by a high fat diet. Regulation of gene expression in these cell types impacts every aspect of metabolism, and our data provide a robust framework recapitulating transcriptional processes affecting multiple cell populations. Our approach is thus complementary to on-going cell type-specific transcriptomic efforts.
For more information, see our paper, which is available for download through eLife: https://elifesciences.org/content/5/e15614.
The full citation to our paper is:
See our blog post on a recent paper reviewing the HMDP data set: http://www.zarlab.xyz/the-hybrid-mouse-diversity-panel-a-resource-for-systems-genetics-analyses-of-metabolic-and-cardiovascular-traits/