In this study, blood cell traits were collected from each strain in the HMDP panel which consists of 100 mouse strains. Using EMMA(10.1534/genetics.107.080101), we identified associations with these traits. The main advantage of the HMDP compared to the traditional genetic cross approach is the increase in resolution of the association.
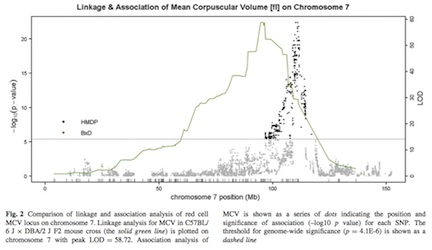
We identified a particularly striking association with mean corpuscular volume (MCV). The figure from the paper shows both the manhattan plot for the HMDP as well as the linkage plot from a genetic cross examining the same trait for chromosome 7. This example clearly shows the advantge of the HMDP compared to the cross in terms of resolution of the association. The peak is less than 1 Mb from Hbb-b1 which has been previously suggested to affect this trait.
Some reviews covering the HMDP and mouse genetics more broadly are available here.
Full Citation:
Davis, Richard C, Atila van Nas, Brian Bennett, Luz Orozco, Calvin Pan, Christoph D Rau, Eleazar Eskin, and Aldons J Lusis. 2013. Genome-wide association mapping of blood cell traits in mice. Mamm Genomedoi:10.1007/s00335-013-9448-0
Abstract:
Genetic variations in blood cell parameters can impact clinical traits. We report here the mapping of blood cell traits in a panel of 100 inbred strains of mice of the Hybrid Mouse Diversity Panel (HMDP) using genome-wide association (GWA). We replicated a locus previously identified in using linkage analysis in several genetic crosses for mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and a number of other red blood cell traits on distal chromosome 7. Our peak for SNP association to MCV occurred in a linkage disequilibrium (LD) block spanning from 109.38 to 111.75 Mb that includes Hbb-b1, the likely causal gene. Altogether, we identified five loci controlling red blood cell traits (on chromosomes 1, 7, 11, 12, and 16), and four of these correspond to loci for red blood cell traits reported in a recent human GWA study. For white blood cells, including granulocytes, monocytes, and lymphocytes, a total of six significant loci were identified on chromosomes 1, 6, 8, 11, 12, and 15. An average of ten candidate genes were found at each locus and those were prioritized by examining functional variants in the HMDP such as missense and expression variants. These results provide intermediate phenotypes and candidate loci for genetic studies of atherosclerosis and cancer as well as inflammatory and immune disorders in mice